Free HTTP(s) Analyzer on the Mihan Monitor
To use the Free HTTP(s) Analyzer on the Mihan Monitor , simply enter your domain or IP address in the appropriate box. Then see the output as follows.
You can register for a continuous check and receive a timely warning at the site and use this powerful tool for free.
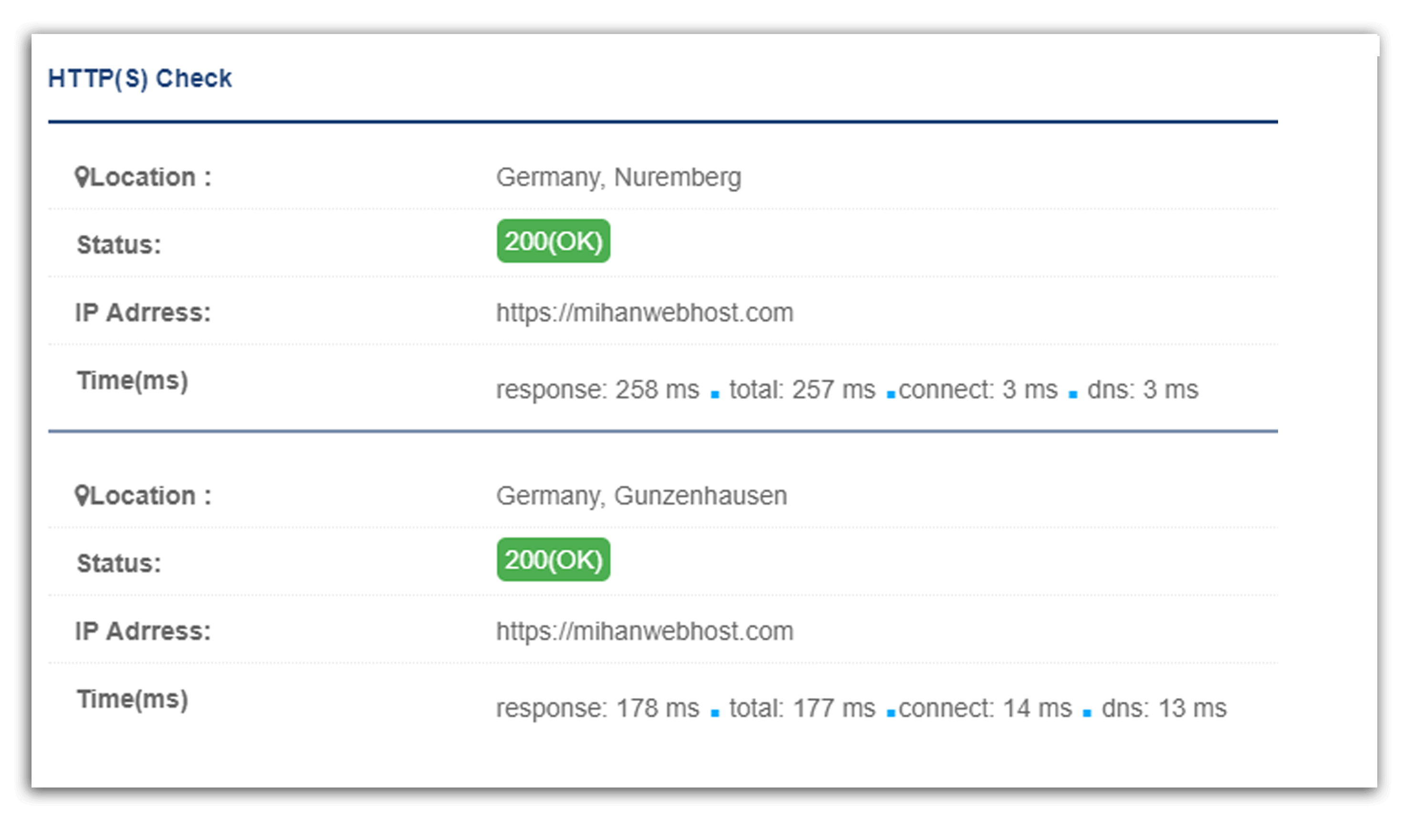
If the domain or IP is enabled and available, as in the image below, you will see 200OK status from each of our nodes.
In the event of a problem with the availability of a domain or IP, one of the following Result is returned.100 (continued) The applicant must continue to apply. The server displays the code when it receives the first part of the request and waits for the rest of the requests.
- 101 (Replacing Protocols) The requestor requests the server to request the switching of the protocols and the server is approving the switching.
- 200 (successful) server has successfully queried the request. This means that the server has provided the requested page.
- 201 (built) is a successful request and the server has created a new source.
- 202 (Accepted) The server accepts the request but has not yet calculated it.
- 203 (Invalid Information) The server successfully calculates the request, but displays information that may be related to another source.
- 204 (without the contents of the server calculates the request successfully, but does not display any content.
- 205 (reset content) The server successfully queries the request, but does not display any content. Unlike Code 204, this code requires that the requestor reset the file view (for example, emptying a form).
- 206 (partial content) The server has successfully processed the partial request.
- 300 (Several choices) The server has ready-made activities based on the request. The server may select an activity on a requesting basis or may list a list of activities that the requester is able to select.
- 301 (Permanent Transfer) The requested page has been permanently transferred to another location. When the server displays this response, it automatically transfers the requester to the new location.
- 302 Temporary Transition) The server is currently responding to page requests at another location, but the requester must continue to use the original location for future requests.
- 303 (Refer to another location) The server displays this code when the requestor needs to receive a separate request for receipt to another place to receive an answer.
- 304 (Uncorrected) Since the last request, the requested page has not been modified. When the server displays this response, the contents of the screen will not be displayed.
- 305 (Use of the proxy) The requester can once access the requested page using the proxy.
- 307 (temporary redirection) This code acts like code 302.
- 400 (Invalid request) The server is unable to recognize syntax.
- 401 (not allowed) request requires authentication. The server may display this response for a single logon login.
- 403 (blocked access) Access from this point is blocked.
- 404 (not found) The server can not find the requested page. For example, if a page that does not exist on a server is requested, the server often displays this code.
- 405 (Not allowed) The specified procedure is not permitted.
- 406 (Not Accepted) The requested page is unable to respond with the requested content properties.
- 407 (Requires proxy authentication). This code is similar to code 401, but specifies that the requester needs to verify the use of the proxy. When the server displays this response, it also means the proxy that the requestor should use.
- 408 (request interruption) Server waiting for request is over.
- 409 (Incompatibility) of the server has encountered incompatibility to perform the request. The server must contain information about the incompatibility of the request.
- 410 (out of reach) The server displays this response when the requested source has been permanently deleted. This code is similar to code 404, but sometimes it is used instead of code 404 for resources that no longer exist.
- 411 (Required length) The request server will not be deleted without the length of the contents of the field.
- 412 (failed precondition) The server does not encounter one of the preconditions that the requestor has made in the request.
- 413 (The request entity is very large) The server is unable to process due to the size of the request to handle.
- 414 (Required Ural is too long) The requested url for processing by the server is very long.
- 415 (media type not supported) The request is not supported by the requesting page.
- 416 (The requested range is not satisfactory) If the request is for a range that is not available for the page, the server displays this status code.
- 417 (Failed Waiting) The server is not able to handle the expected field header.
- 500 (internal server error) The server is encountering an error and is unable to execute the request.
- 501 (not running) server does not have the ability to perform the request. For example, the server may display this code when it is unable to identify the request method.
- 502 (bad port) server acts like a port or proxy and received an incorrect response from the top server.
- 503 (Service not available) The server is currently unavailable. (Because of repair or expensive or disabled). In general, this is a temporary situation.
- 504 (server interruptions) server acts like a port or proxy and has not received a timely request from the server.
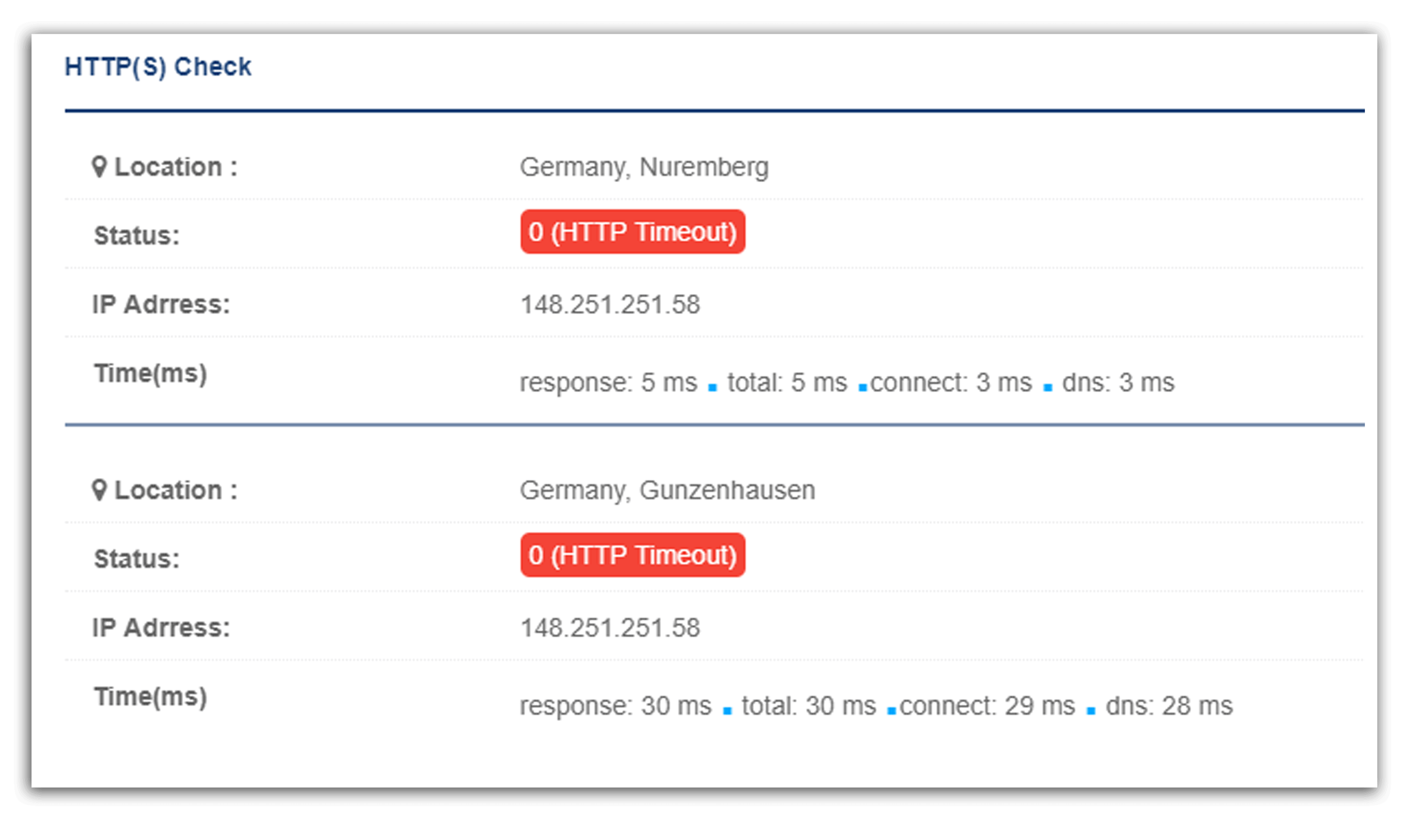
And in the absence of the site, as in the image Result 0 is returned.
Experience the free HTTP (s) analytics tool on the Mihan Monitor with the web host’s monitoring service.
How useful was this training?

